Tunnel lighting is a critical component of road safety, as it allows drivers to navigate through tunnels safely and efficiently. The requirements for tunnel lighting can vary depending on the specific location within the tunnel, such as the entrance, middle section, or exit. In this article, we will examine the different lighting requirements for each of these areas and how AGC, a manufacturer of lighting solutions, can meet these specific needs.
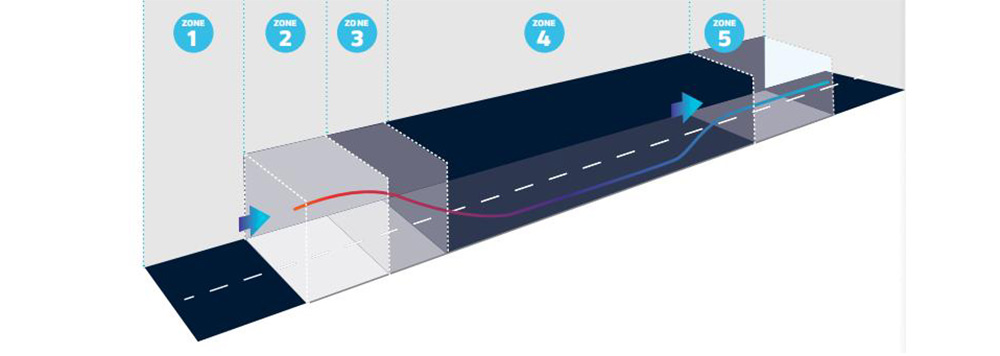
1. Ready to enter
The area leading to the tunnel entrance Drivers must be able to identify obstacles. AGC recommends using LED luminaires with a Medium wattage, for example, 200-300 watts.
2. Entrance Lighting
The entrance to a tunnel is a particularly important area for lighting, as it serves as the transition zone between the outside environment and the tunnel. The lighting in this area should be bright enough to allow drivers to adjust their eyes to the change in lighting conditions without causing glare or discomfort. Tunnel entrance Maintaining the uniformity in luminance between the access area and this zone prevents the black hole effect.
AGC recommends using LED luminaires with high power, for example, up to 450W or 570W.
3. Transition Area Lighting
The second part of the tunnel comes directly after the threshold zone.
Progressively reduce the luminance to allow the human eye to adapt.
Provide the right levels to enable adaptation.
AGC recommends using LED luminaires with a Medium wattage, for example, 200-300 watts.
4. Middle Section Lighting
The middle section of a tunnel is typically the longest and most uniform section, and the lighting requirements for this area can vary depending on the length of the tunnel and the speed of traffic. AGC recommends using LED luminaires with a power rating of 40-150 watts for this area. These luminaires should be designed to provide uniform light distribution throughout the tunnel with minimal light spillage outside the tunnel.
5. Exit Lighting
The exit of a tunnel is another crucial area for lighting, as it serves as the transition zone between the tunnel and the outside environment. The last section of the tunnel Increased the luminance level to bright enough to allow drivers to adjust their eyes to the change in lighting conditions without causing glare or discomfort.
AGC recommends using LED luminaires with high power, for example, up to 450W or 570W.
Consideration for tunnel lighting
When it comes to selecting lighting solutions for tunnels, there are several key factors to consider, including power. These include:
1. Power rating: The power rating of the lighting fixtures will depend on their specific location within the tunnel. As discussed earlier, the entrance, middle section, and exit may all require different power ratings to provide adequate illumination without causing discomfort or glare for drivers.
2. Uniformity of light distribution: It's essential to select lighting fixtures that provide even light distribution throughout the tunnel to minimize the risk of dark spots or bright spots that could impair drivers' vision.
3. Color rendering index (CRI): A high CRI is important for tunnel lighting to ensure that drivers can accurately distinguish between different objects and hazards within the tunnel.
4. Energy efficiency: As with any lighting application, it's important to select energy-efficient solutions to minimize energy consumption and costs while reducing the environmental impact of the lighting system.
In short, EVERY TUNNEL IS UNIQUE AND SO IS THE WAY TO LIGHT IT.

Related video:












