LED lighting has become the preferred choice for many applications due to its energy efficiency, long lifespan, and versatility. However, LEDs are highly sensitive to temperature variations.
Extreme temperatures, whether excessive heat trapped in enclosed fixtures or freezing outdoor conditions pose challenges for LED operation. Rapid temperature fluctuations, such as in environments like mining sites, further complicate their performance, potentially leading to reduced efficiency, premature failure, or fluctuations in light output.
In this blog, we will explore how temperature fluctuations affect LED lighting, the challenges they pose, and the solutions to ensure optimal performance in varying conditions.
- Environment with temperature fluctuations pose challenges for LED lights
- Impacts of temperature fluctuations on LED lights
- Heat can degrade LED performance and lifespan
- Cold environments can delay the startup
- Temperature fluctuations can cause mechanical damage
- Solutions to protect LED lights from temperature fluctuations
Environment with temperature fluctuations pose challenges for LED lights
Temperature fluctuations, such as rapid shifts between hot and cold, can occur due to various factors, including changing weather patterns and internal environmental conditions. In outdoor settings, industrial sites, and even specific indoor applications, these fluctuations push LED lighting to its limits.
Whether sudden or gradual, temperature variations introduce stress that can compromise the delicate components of LED lights. For example, outdoor lighting fixtures may experience scorching 40°C summer days followed by sub-zero winter nights. In industrial environments, such as oil rigs and mining sites, temperatures can range from freezing at night to extreme heat during the day.
These fluctuations can cause mechanical strain that can lead to cracks, material degradation, and overall performance deterioration of the LED lighting system.
Impacts of temperature fluctuations on LED lights
LEDs are highly sensitive to temperature changes. Extreme heat, cold, or rapid temperature fluctuations can affect their performance, lifespan, and overall reliability.
Heat can degrade LED performance and lifespan
LEDs operate optimally within a specific temperature range, typically between 25°C and 85°C. If the ambient temperature rises too high or thermal management is inadequate, the junction temperature of the LED can exceed safe limits. This can lead to immediate and accelerating performance degradation.
At elevated temperatures, the quantum efficiency of the LED decreases, meaning fewer photons are generated per electron-hole recombination event. In simple terms, this results in reduced light output (lumen depreciation) despite the same power input.
Excessive heat also speeds up the chemical degradation of encapsulants and packaging materials, causing them to yellow, crack, or delaminate, which further reduces light quality and intensity. Industry studies suggest that for every 10°C increase in operating temperature, LED lifespan may decrease by 30-50%.
High temperatures can also affect electronic components such as drivers and circuits, potentially leading to malfunctions, flickering, or complete failure of the lighting system.

Cold environments can delay the startup
LEDs perform well in cold environments and often outlast traditional lighting in such conditions. However, at extremely low temperatures (below -30°C), certain components within the LED driver, such as capacitors and transistors, can experience increased resistance, altered capacitance, and reduced switching efficiency. This can lead to a noticeable delay in reaching full brightness and, in some cases, erratic behavior during startup.
A more serious concern is condensation formation during sudden temperature transitions. When a cold LED fixture rapidly warms up, moisture can condense on electrical components, increasing the risk of short circuits and accelerated corrosion, which may compromise the fixture’s longevity and reliability.

Temperature fluctuations can cause mechanical damage
One of the most overlooked impacts of temperature fluctuations is mechanical stress caused by thermal shock, rapid temperature changes that make different materials expand and contract at varying rates.
These uneven expansion and contraction cycles create shear stress at material interfaces, leading to structural weaknesses over time. Repeated thermal cycling can result in solder joint fatigue, wire bond fractures, die-attach delamination, and cracks in lenses.
Thermal shock accelerates wear and tear, increasing the likelihood of early failures in LED fixtures.
Solutions to protect LED lights from temperature fluctuations
LED lighting fixtures must be designed to withstand extreme temperature variations, from freezing cold to intense heat. At AGC, most of our products operate reliably within a temperature range of -30°C to 50°C, with some products capable of functioning in temperatures as high as 70°C.
To ensure stable performance and long-lasting durability under fluctuating temperatures, consider the following solutions:
Use durable materials
In environments with significant temperature variations, lighting systems must be constructed from materials that can ensure both heat and cold.
For optimal LED performance, efficient heat dissipation is essential. During operation, LEDs generate heat that must be quickly dispersed to prevent damage. A PCB with an aluminum layer is an excellent choice, as it offers high thermal conductivity and effectively transfers heat away from the LED.
For high-temperature environments, like steel mills, use heat-resistant materials such as high-grade metals and incorporate advanced heat-dissipating components to prevent overheating. For cold environments, choose corrosion-resistant materials like low-copper aluminum to prevent moisture-related degradation and ensure long-term durability.
Protective seals and enclosures also play a crucial role in shielding sensitive components from harsh environmental conditions. Using tempered glass panels or lenses instead of PC is recommended, as tempered glass is more resistant to temperature fluctuation and less prone to burning or cracking.
Thermal management
The key to thermal management starts with efficient heat dissipation.
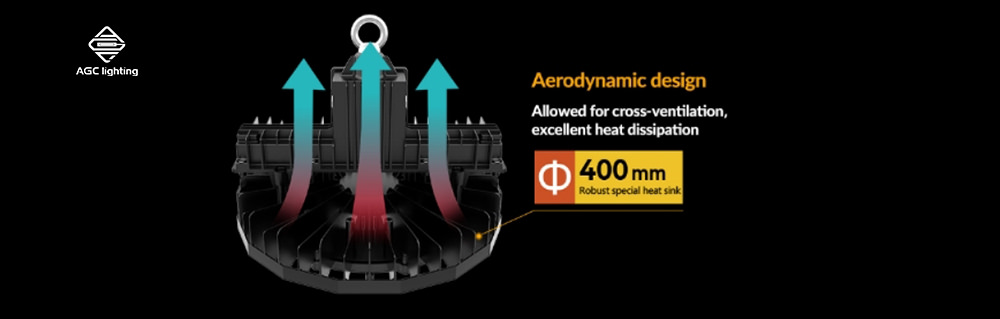
A high-quality aluminum heat sink is a common choice due to its excellent thermal conductivity. The larger the heat sink, the better its performance, especially when designed with higher fin density and increased surface area to maximize heat dissipation.
For example, our HB31 high bay light features a large heat sink and hollow design for fast heat dissipation. With the advanced thermal management, the HB31 can operate in ultra-high temperatures of up to 70°C.
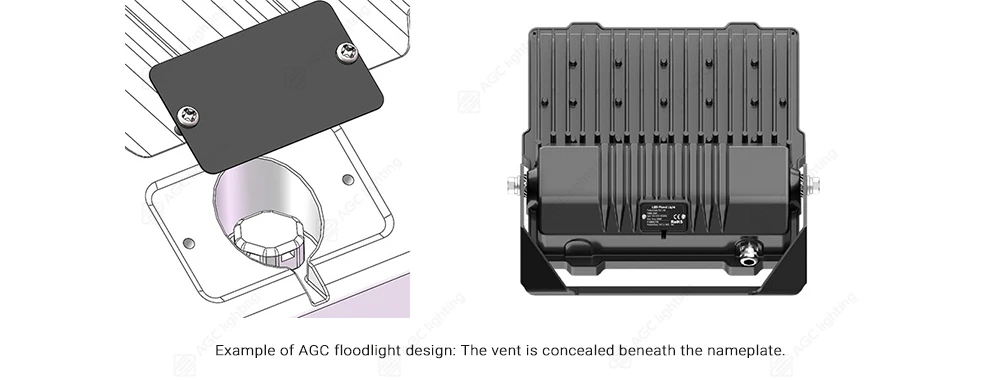
Except for heat sinks, another critical element in managing temperature fluctuations is the vent. A well-designed vent can help ensure proper airflow, preventing excessive heat buildup. It also equalizes pressure between the fixture’s interior and the external environment, reducing condensation risks. With moisture control, the lighting system can maintain stable performance. Here is an example of the vent design of our floodlight.
Power supply system
The long-term reliability of LED lighting fixtures depends on the electronic components, particularly the power supply system. Selecting weather-resistant wires and drivers is essential to ensure stable performance in extreme conditions.
Many LED drivers are not hard to start up in extremely low temperatures, which can lead to system failures. Moreover, the cold temperatures can make wires brittle, increasing the risk of breakage. In a project, our customer required the lighting fixtures to work well at -40°C. We used a power supply rated for as low as -55°C, ensuring smooth and safe operation in extreme cold.

Excess heat also can degrade electronic components and reduce efficiency. Isolated driver is recommended. This type of driver reduces heat buildup, enhances heat dissipation, and is better suited for high-temperature locations.
Installation and placement
Whenever possible, install fixtures away from additional heat sources, such as machinery and industrial equipment to prevent excessive heat buildup. Avoid placing fixtures in areas with direct sunlight or cold drafts, as extreme exposure can impact performance. But for outdoor lighting, exposure to temperature extreme is often unavoidable. Therefore, material selection and thermal management are critical.
Adequate spacing between fixtures allows for better airflow and heat dissipation, reducing the risk of overheating. This also helps maintain uniform illumination and prevents concentrated heat zones that could degrade LED performance over time.












