LED lighting has become the primary light source today, and at the heart of these systems are LED drivers. These components play a crucial role in determining whether your LEDs will provide consistent illumination for years or become a frequent maintenance issue. Essentially, the type of LED driver you choose impacts the overall performance, efficiency, and lifespan of the lighting system.
But have you ever considered what type of LED driver your lighting fixtures use? There are two main types: constant current drivers and constant voltage drivers. Understanding the difference between these two is essential to ensure your lighting fixtures operate effectively. So, which one is right for your needs? Let’s explore this together.
What is an LED driver
Let’s start by understanding the LED driver. An LED driver is a crucial component responsible for powering and controlling LED lights. It regulates the electrical power supplied to the LEDs, ensuring consistent performance and protecting them from damage.
LEDs require a stable direct current (DC) to function properly, but most power sources supply alternating current (AC). The LED driver converts this AC power into the necessary DC power. Additionally, LEDs are highly sensitive to changes in current, and even slight variations can affect their brightness. The LED driver manages the current flowing through the LEDs, preventing them from drawing too much, which helps maintain consistent brightness and prevents overheating. Since LEDs generate heat during operation, this regulation is vital to ensure their longevity and efficiency.

What is a constant current LED driver?
A constant current (CC) LED driver is a power supply that ensures a steady current flows through LEDs, regardless of voltage changes. To simplify, think of it like water flowing through a pipe. LEDs are like water wheels that need a specific amount of water to spin efficiently and shine brightly. A CC driver acts like a pump that maintains a consistent water flow, adjusting the pressure as needed. In electrical terms, it keeps the current steady by adjusting the voltage.
The primary advantage of a CC driver is its ability to provide a constant current, which results in uniform brightness across LEDs and improves overall efficiency. It also helps prevent thermal runaway. The excessive current can increase the temperature, potentially shortening the LED's lifespan.
However, CC drivers are generally used for LEDs connected in a series circuit. This setup has a downside: if one LED fails, the entire string goes out. Additionally, designing a system with CC drivers can be more complex than using constant voltage systems. It requires careful planning to ensure each LED receives the correct current.
What is a constant voltage LED driver?
A constant voltage (CV) LED driver functions as a steady power source for LED lights, supplying a steady voltage, typically 12V or 24V DC. It converts standard electricity into the lower voltage required by LEDs, ensuring the voltage remains constant regardless of how much current the LEDs draw.
However, CV drivers have some limitations. Without proper safeguards, they can potentially damage LEDs. A slight change in voltage can lead to an excessive increase in current, which may reduce the lifespan of the LEDs. To prevent this, additional components like resistors are often used to regulate the current. Despite these precautions, CV drivers are generally more cost-effective than CC drivers, making them a popular choice for many lighting applications.
Key differences between constant current and constant voltage drivers
In short, constant current drivers provide a steady current while constant voltage drivers maintain a fixed voltage. Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
|
Feature |
Constant Current (CC) Driver |
Constant Voltage (CV) Driver |
|
Output |
Fixed current, variable voltage |
Fixed voltage, variable current |
|
Connection type |
Series |
Parallel (typically with resistors) |
|
Benefits |
Prevent overheating, extend LED lifespan |
Easy installation and scalability |
|
Risks |
Single LED failure affects all LEDs in series |
Potential damage if current is unregulated |
|
Complexity |
More complex |
Simpler |
|
Cost |
Generally higher |
Generally lower |
Choosing the right driver for your needs
Choosing the right fixture and driver is crucial to making sure LEDs get the correct amount of current and voltage. A good driver helps maintain the LED's performance and prevents problems like overheating or short circuits, providing safe, flicker-free, and efficient lighting.
When deciding between constant voltage and constant current drivers, it depends on what your LED application needs. Let's break down the power formula:
Power = Current x Voltage (P = I x V)
At first glance, if the voltage and current for an LED are fixed, the power stays the same. This might make it seem like choosing between a constant voltage or constant current driver doesn't matter. However, there's a key detail to consider: LEDs' voltage and current characteristics change with temperature.
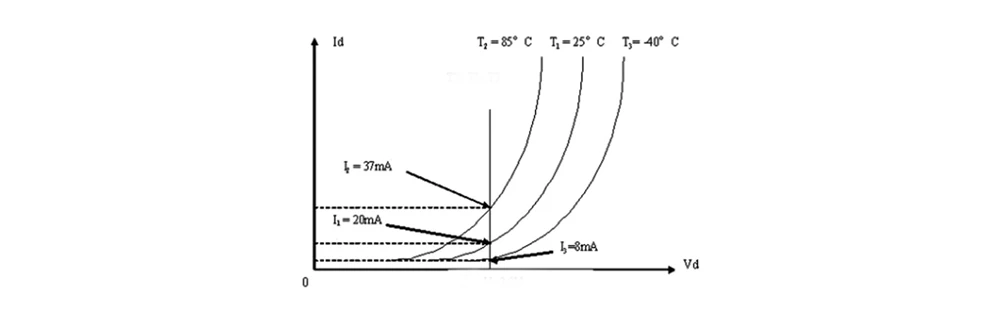
LEDs generate heat when they’re on, and they have what's called a negative temperature coefficient. This means that as the temperature goes up, the current increases even if the voltage stays the same. This happens because the electrical resistance of the LED decreases as it gets hotter, causing more current to flow. So, using a constant voltage driver can lead to fluctuating current levels, which might cause overheating and inconsistent performance.
To handle this, a constant current driver is usually a better choice. It keeps the current steady, even when voltage changes due to temperature shifts. This ensures stable operation, consistent brightness, and helps the LEDs last longer. Constant current drivers are great for high-power LEDs and applications where consistent brightness is important, like street lighting, outdoor lighting, industrial lighting, and retail lighting.
On the other hand, constant voltage LED drivers are better for setups where LEDs are connected in parallel, like LED strips, signs, and architectural lighting. They provide a stable voltage, making it easier to connect multiple LEDs and use different types of LEDs. This makes constant voltage drivers perfect for situations where you need to power several LEDs efficiently and with straightforward installation.
What if neither constant current (CC) nor constant voltage (CV) drivers are suitable for your lighting project? Both CC and CV drivers have their limitations, which may not meet the specific requirements of certain applications. In such cases, a constant power LED driver might be the ideal solution.
A constant power LED driver regulates both the output voltage and current to deliver a consistent level of power to the LED. This ensures that the LED operates at its optimal performance, providing the desired light output while maintaining an appropriate junction temperature.
If you'd like more information, please contact us.