An LED driver is essential for the proper operation and performance of LED lighting systems. It is an electronic device that regulates the power and current to an LED lighting system. Therefore, choosing the LED lights with the right LED driver is critical for the safety of your lighting projects. But do you know the difference between Class I, Class II Class 1, and Class 2 LED drivers? If not, you might be missing out some important information that could affect the safety and performance of your lighting system. In this blog post, you will have a clear understanding of the differences between these classes and how they relate to various standards and regulations. By understanding these difference, you will be able to make better decision for LED fixtures. Read on and discover the answers to your questions.
What is an LED driver
LED drivers are also known as LED power supplies. They have similar function as the ballasts for fluorescent lamps. They ensure the proper operation and performance of LEDs. LED drivers are responsible for converting the incoming AC voltage to a DC voltage that is suitable for powering the LED lights. They provide the correct voltage and current levels for LEDs and protect them from voltage fluctuations and power surges. There are different types of LED drivers, such as constant current, constant voltage, dimmable and non-dimmable. The type of LED driver you need depends on your needs. For example, if you want to control the brightness of your LED lights, you need a dimmable LED driver that can adjust the output voltage or current according to a signal from a dimmer switch.

Difference between classes
One of the factors that affects the choice of LED driver is the class of driver. According to different standards, LED drivers are classified as Class 1 and Class 2 or Class I, Class II, and Class III. Confusion often exists regarding to the difference between Class 1 and Class 2, and Class I and Class II.
Class 1 and Class 2 denote compliance with NEC (National Electric Code). It stands for the output voltage and power capabilities of AC-DC supplies. LED drivers listed with Class I, Class II, and Class III comply with IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission). It refers to a power supply’s internal construction and electrical insulation.
|
Classification |
Class 1, Class 2 |
Class I, Class II, and Class III |
|
Authority |
NEC |
IEC |
|
Insulation |
Electrical limitation |
Internal construction and electrical insulation |
Class 1 vs Class 2
LED drivers are devices that regulate the power supply to an LED light source. They are classified according to UL standards for safety and performance. Two such classifications are UL Class 1 and UL Class 2, which have different implications for the design and installation of LED lighting systems.
UL Class 1 drivers have output ranges outside of UL Class 2 designations. They have a high-voltage output and require safety protection within the fixture. Class 1 drivers can accommodate more LEDs, making them more efficient than Class 2 drivers. However, they also pose a higher risk of fire or electric shock if not properly installed or insulated. The wiring methods for Class 1 drivers must comply with NEC (National Electric Code) requirements for power circuits.
UL Class 2 drivers comply with standard UL1310, meaning their output is considered safe to contact and no major safety protection is required at the LED/luminaire level. There is no risk of fire or electric shock from these drivers. They operate using less than 60 volts in dry applications, 30 volts in wet applications, less than 5 amps, and less than 100 watts. However, these limitations restrict the number of LEDs a Class 2 driver can operate. The wiring methods for Class 2 drivers are less stringent than for Class 1 drivers and can use smaller gauge wires and connectors.
In summary, UL Class 1 and UL Class 2 LED drivers have different output ranges, safety features, efficiency levels, and wiring methods.
|
Classification |
Class 1 |
Class 2 |
|
Authority |
NEC |
NEC |
|
Symbol |
UL |
UL |
|
Feature |
Power≤1000 Volt-Amps |
Voltage≤60 (Dry); Voltage≤30(Wet) |
|
Application |
High power or long runs of LED lights |
Low power or short runs of LED lights |
Class I vs Class II
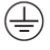
Class I power supplies have basic insulation and a protective earth (ground) connection. Basic insulation is a layer of material that prevents direct contact with live parts. A protective earth connection is a wire that connects the metal chassis of the power supply to the ground. This provides a path for the fault current to flow to the ground in case of insulation failure, and triggers a circuit breaker or a fuse to cut off the power supply. Class I power supplies require a three-wire power cord with a safety earth connection.
Class II power supplies have double insulation or reinforced insulation, and no protective earth connection. Double insulation is a combination of basic insulation and supplemental insulation, which is another layer of material that covers the basic insulation. Reinforced insulation is a single layer of material that provides the same level of protection as double insulation. Both double and reinforced insulation prevent electric shock even if one layer of insulation fails. Class II power supplies do not need a protective earth connection because they have higher insulation levels. They use a two-wire power cord without a safety earth connection. Class II has the concentric square symbol on the safety label.
The main difference between Class II and Class I power supplies is the type and level of insulation they use, and whether they need a protective earth connection or not. Class II power supplies have higher insulation levels and no earthing, while Class I power supplies have lower insulation levels and earthing. Both classes provide adequate protection from electric shock, but they have different applications and requirements.
|
Classification |
Class I |
Class II |
|
Authority |
IEC |
IEC |
|
Symbol |
|
|
|
Feature |
Three-wire power cord |
Two-wire power cord |
|
Protective earth connection |
Yes |
No |
If you have any questions or need further assistance, don't hesitate to contact us.