As cities transform into smart ecosystems, efficient street lighting has become imperative for enhancing safety and sustainability. Smart street lights stand out as the cornerstone of smart cities, offering benefits ranging from energy savings to improved public safety. But with a variety of network protocols available, selecting the right one for your lighting projects can be a challenge. Among these technologies for smart lighting, LoRa, Zigbee, and NB-IoT/CAT1 are the three common protocols.
In this blog post, we will explore their strengths, weaknesses, and ideal applications to help you make an informed decision for the lighting project.
- Benefits of Smart Street Lights
- Smart Street Light Network Solutions
- LoRa: Long Range, Low Cost
- Zigbee: Multi-nodes, Short Distance
- NB-IoT/CAT1: Single Point, Long Distance
- Difference Between Zigbee, LoRA, and NB-IoT/CAT1
- Management and Control Center of Smart Lighting
- Controller Options: NEMA and ZHAGA Sockets
Benefits of Smart Street Lights
- Improve public safety: Brighter and more strategically placed lighting deters crime by increasing visibility for pedestrians and reducing dark areas.
- Environmental sustainability: Smart street lights can be dimmed or turned off entirely for specific needs, leading to significant energy consumption reduction and lower carbon footprints. For example, operators can adjust street lights to lower intensity in low-traffic areas.
- Higher operational efficiency: Street lights can be monitored and controlled remotely. This allows for quicker and more flexible control. The data collected in smart lighting systems can be used to predict potential failures. Then, operators can schedule preventative maintenance, minimizing downtime.
Smart Street Light Network Solutions
LoRa: Long Range, Low Cost
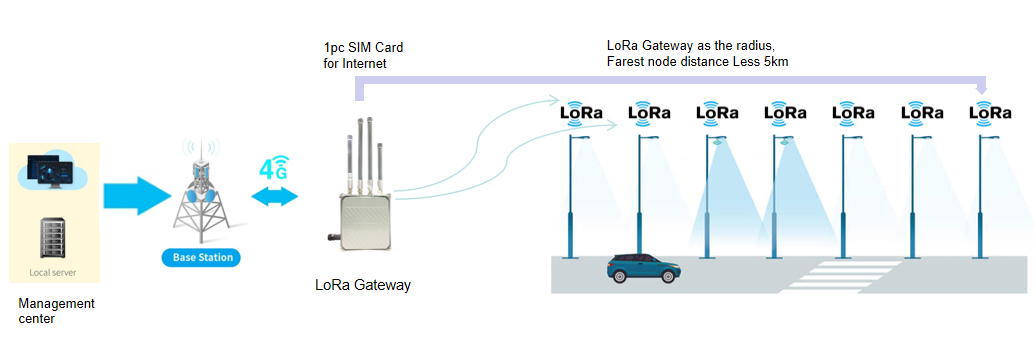
LoRa or LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a communication protocol specifically designed for long-range, low-power applications like smart street lights.
Advantages of LoRa
It offers several advantages for connecting street lights in small and medium-sized cities.
- Reduce subscription fees: One of the significant advantages of LoRaWAN is its cost-effectiveness. Unlike cellular networks like NB-IoT/CAT1 which require individual SIM cards for each node, LoRaWAN only necessitates a few SIM cards for the gateways. This translates to significant savings on subscription fees as the number of nodes increases.
- Long-range connectivity: LoRaWAN supports a communication distance of up to 1-3 KM in urban environments, ideal for covering large areas. It needs fewer gateways compared to other protocols like Zigbee or Bluetooth.
Key points about LoRa for smart street lights
- Gateway installation: For optimal performance, LoRaWAN gateways should be installed at least 10 meters high.
- Network range: The maximum distance between a gateway and a node (street light) can reach 2-5km in open spaces.
- Network capacity: A single LoRaWAN gateway can connect with 100-120 nodes, making it suitable for medium-density deployments.
- Centralized control: LoRaWAN requires a single gateway connected to the internet for users to remotely monitor and control all connected street lights.
- Scalability: While LoRaWAN offers excellent range and low power consumption, signal strength can be affected by obstacles and complex environments. In such situations, additional gateways might be necessary to ensure reliable network coverage.
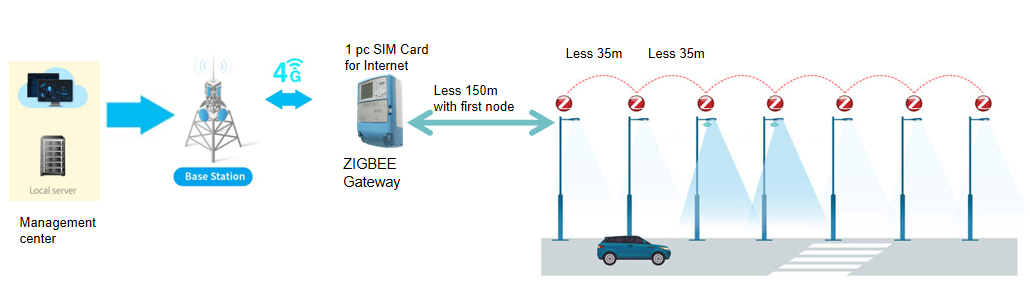
Zigbee: Multi-nodes, Short Distance
Zigbee is a popular networking protocol ideal for short-distance communication in controlled environments like smart street lights. The image shows a scenario where the Zigbee mesh network has excellent performance.
Advantages of Zigbee
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Zigbee networks require a gateway connected to the internet, enabling users to remotely monitor and manage streetlights. This centralized control ensures efficient operation and maintenance of the lighting system.
- Cost-Effective Scalability: Zigbee networks offer scalability without incurring significant costs. With only a few SIM card subscriptions required based on the number of gateways, the overall investment remains manageable even as the network expands.
Disadvantages of Zigbee
- Environmental Considerations: Zigbee's performance can be affected by obstacles and complex environments. Careful planning and potentially additional gateways might be necessary to ensure reliable signal strength in such situations.
- Single Point of Failure: The reliance on a centralized concentrator introduces a potential vulnerability. If the concentrator malfunctions, all connected lights under its purview may lose connectivity. Additionally, failures in intermediary nodes could disrupt the operation of adjacent nodes, impacting the overall network performance.
Considerations about Zigbee for smart street light
For optimal operation, it's crucial to maintain a distance of 150 meters or less between the Zigbee gateway and the nearest node, ensuring unobstructed communication. Beyond this range, employing additional Zigbee nodes as relays becomes necessary, ideally spaced around 35 meters apart. This strategic deployment allows the gateway to effectively cover a radius of 1.5 kilometers, making it suitable for diverse settings such as small towns, communities, or industrial parks, especially when installed along well-lit thoroughfares.
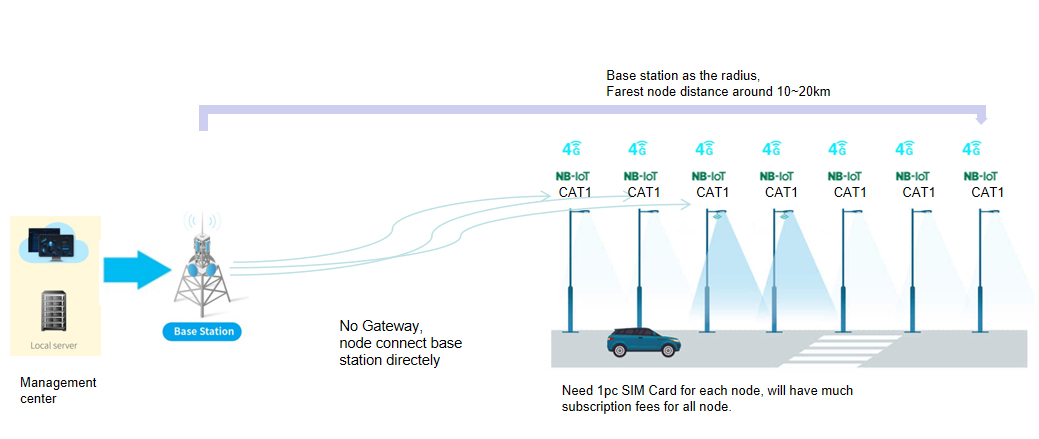
NB-IoT/CAT1: Single Point, Long Distance
NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things) and CAT1 are cellular network protocols designed for long-range, low-power communication. While offering distinct advantages, they also come with a significant cost consideration for smart street lights.
Advantages of NB-IoT/CAT1
- Unmatched Range: NB-IoT/CAT1 has long-range capabilities, with signal transmission reaching up to 10-15 kilometers. This makes them ideal for connecting street lights in vast, particularly sparsely populated areas where other protocols might struggle.
- No Gateway Required: Unlike LoRaWAN and Zigbee, NB-IoT/CAT1 eliminates the need for additional gateways by directly connecting each street light to existing cellular base stations. This can simplify network setup.
- High Signal Reliability: Leveraging established cellular infrastructure, NB-IoT/CAT1 offers robust and reliable signal transmission.
Disadvantages of NB-IoT/CAT1
- Subscription Costs: The biggest drawback of NB-IoT/CAT1 is the requirement for a separate SIM card for each individual street light. This can lead to substantial recurring costs for large-scale deployments compared to protocols requiring fewer gateways.
Difference Between Zigbee, LoRA, and NB-IoT/CAT1
|
Communication Types Comparison |
||||
|
|
Zigbee |
LoRa |
NB-IOT |
CAT.1 |
|
Networking mode |
Based on Zigbee gateway |
Based on LoRa gateway |
Based on the operator base station |
Based on the operator base station |
|
Network Wiring Mode |
No wiring |
No wiring (Gateway deployment location requirement is high, and many factors need to be considered) |
No wiring |
No wiring |
|
Transmission Distance |
Short to Middle (100m-2km level, network relay available ) |
Middle or Remote (Theoretically, it can reach more than 10 km, related to speed rate and antenna gain, and generally 2-5km) |
Remote (Up to ten km, generally above 10km) |
Remote (Up to ten km, generally above 10km) |
|
Capacity of the Single-network Access Node |
over 60,000, generally 200~500 |
About 60,000, the actual numbers are influenced by gateway channels, frequency of node contracting, packet size, and so on. Generally 500 ~ 5,000 |
About 200,000 |
About 50,000 |
|
Frequency Band |
2.4G |
Sub-GHZ(470, 868, 915 MHz.etc) |
Domestic operator frequency band |
LTE-FDD: B1/B3/B5/B8 LTE-TDD: B34/B38/B39/B40/B41 GSM: 900/1800MHz
|
|
Transmission speed |
250kps |
0.3~50kbps |
Theoretically 160kbp ~ 250Kbps, generally less than 100kbps, limited low speed communication interface UART |
Theoretically more than: 10Mbps Less than: 5Mbps Lighting lamp control application is about 80M/ years
|
|
Network Delay |
Less than 1S |
2-3S |
1s -5s |
1s -5s |
|
Application |
Multi-node field scene |
Complicated scene |
Single-point transmission of a discrete type |
Single-point transmission of a discrete type |
|
Communication Type |
LAN |
WAN |
WAN |
WAN |
Management and Control Center of Smart Lighting
Regardless of the chosen network protocol (Zigbee, LoRaWAN, or NB-IoT/CAT1), a central management system is critical for efficient operation and maximizing the benefits of smart street lights. This system acts as the control center, providing vital functionalities for managing and optimizing your smart street lighting infrastructure.
Here are some key features of a Smart Lighting Management System:
- Energy Consumption Analysis: Gain insights into energy usage patterns of individual lights or groups. Identify areas for optimization and potential cost savings.
- Fault Alarm: Receive real-time alerts for any malfunctions or outages in the network, allowing for prompt response and repairs.
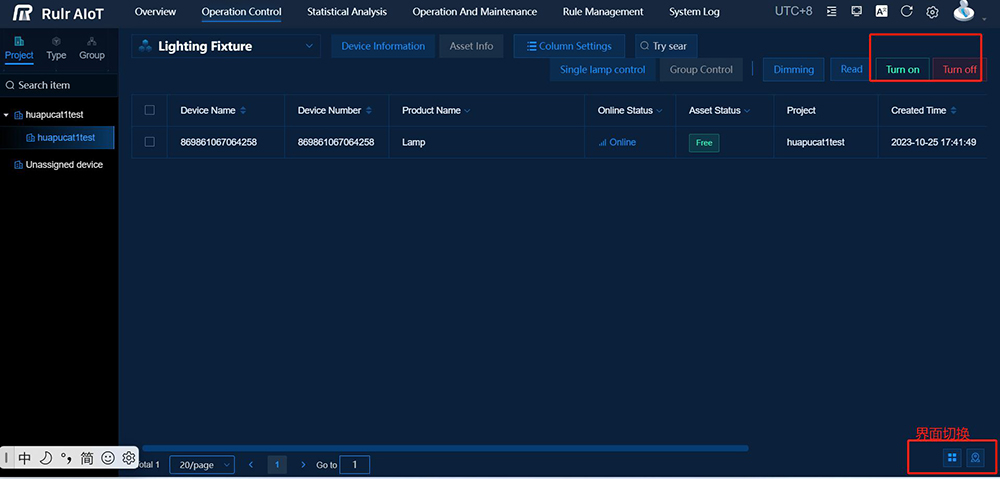
- Street Lamp Control: Remotely control individual lights or groups. Adjust brightness levels, turn lights on/off based on schedules or sensors, and implement dimming strategies.
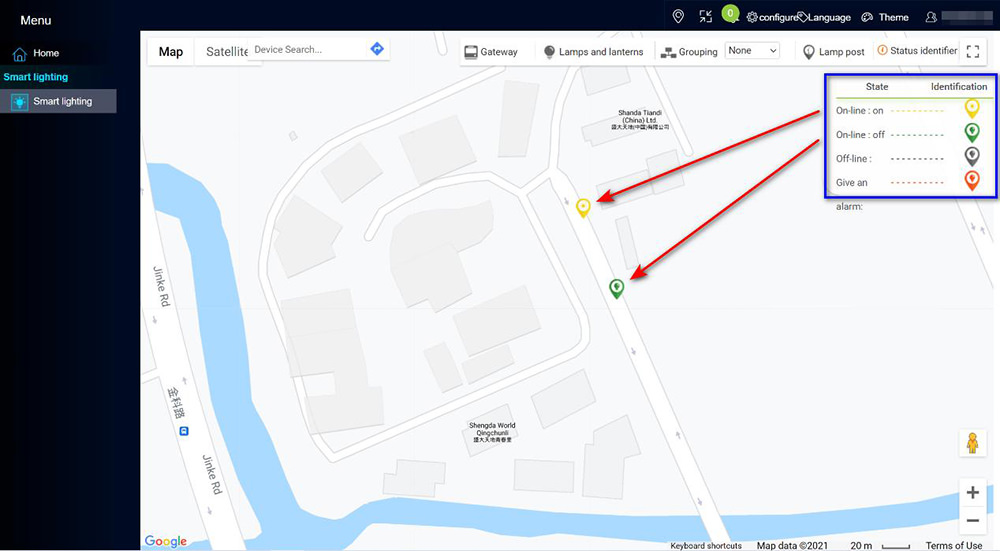
- Map Monitoring (GPS Function): Visualize the location of all connected street lights on a map interface. Utilize GPS data to track their status, optimize maintenance routes, and simplify asset management.
- Remote Meter Reading: Collects energy consumption data from individual lights remotely, eliminating the need for manual meter readings.
- Strategic Management Functions: The system can provide valuable data for strategic planning, allowing for informed decisions about network expansion, maintenance scheduling, and resource allocation.
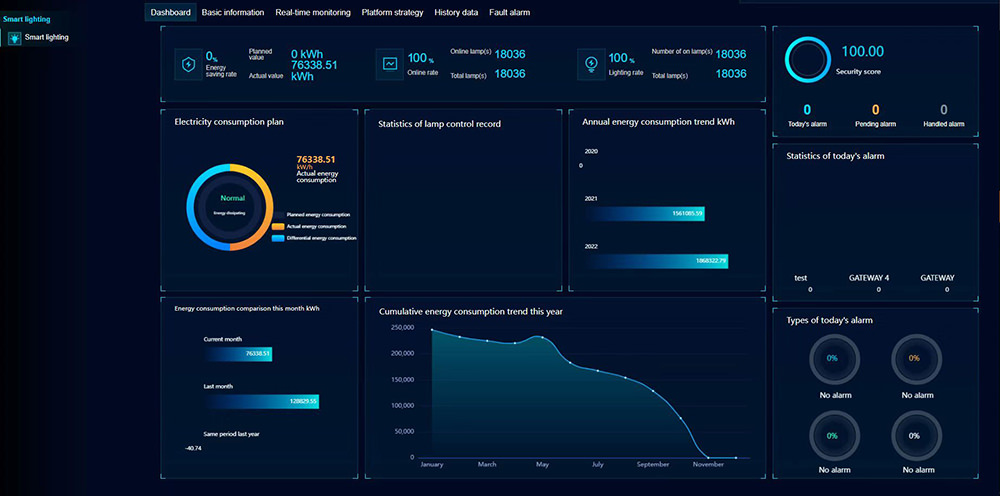
Below is an example smart lighting management system:
Smart Lighting Dashboard
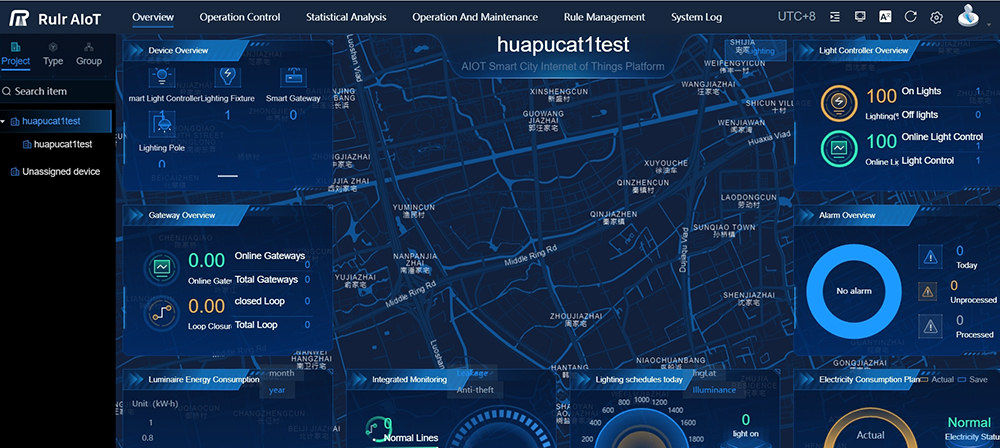
Map Monitoring and Control (Shanghai as an example ):
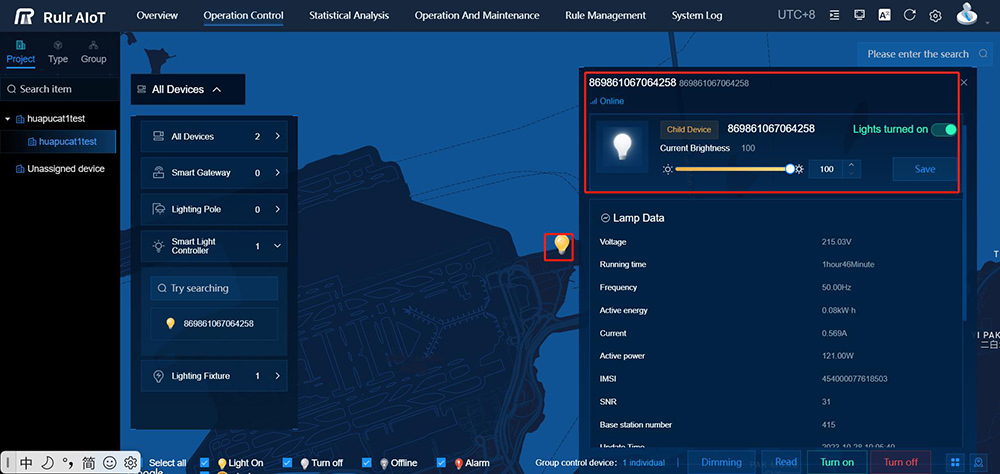
Real-time Monitoring and Control
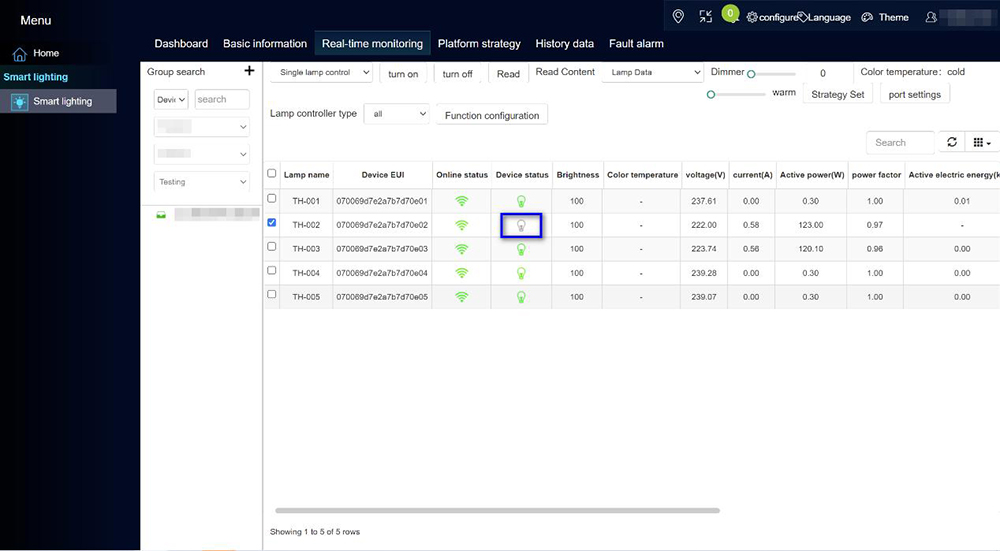
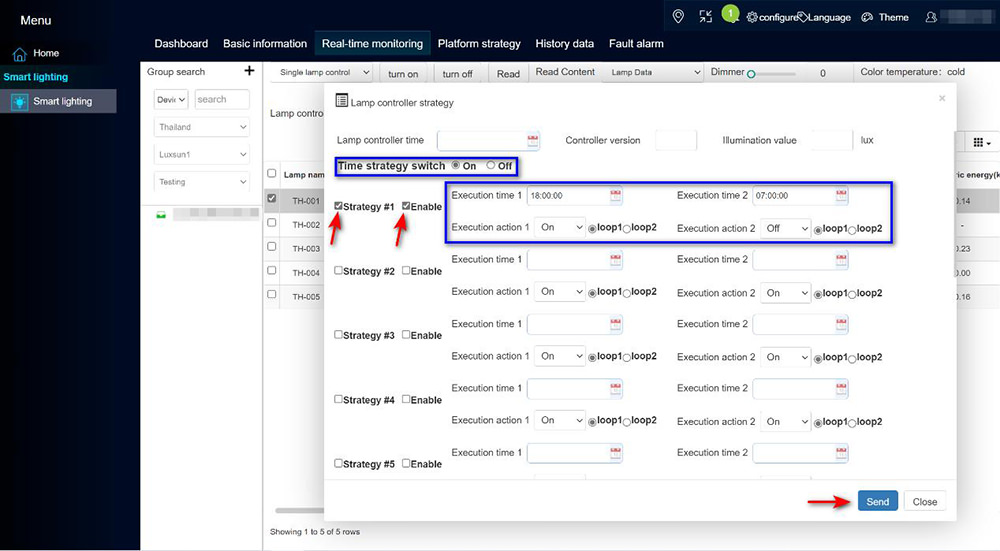
Lighting Schedules
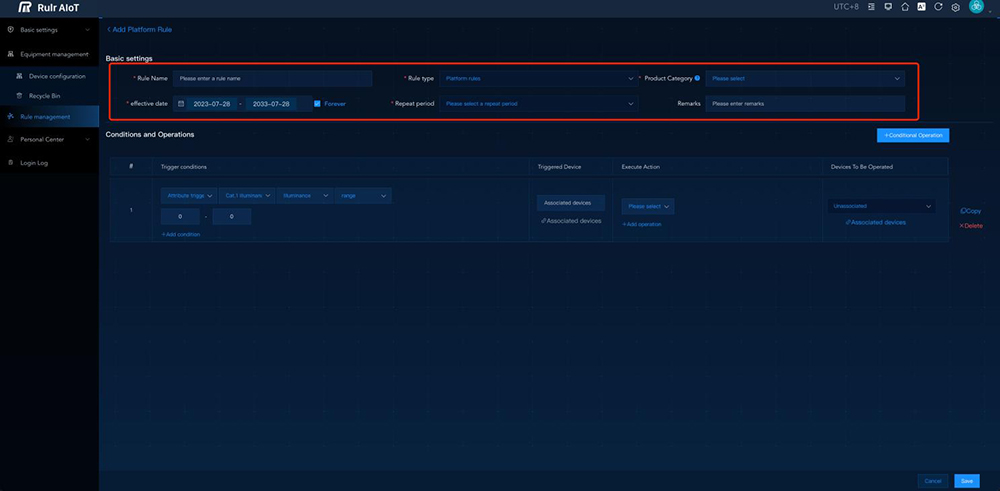
Controller Options: NEMA and ZHAGA Sockets
The choice of controller plays an important role in ensuring seamless integration, functionality, and efficiency. We provide both NEMA and ZHAGA sockets to ensure the compatibility of your lighting project.


Looking for solutions for your smart street light project? Contact us now!













