In today’s cities, street lighting is more than just illumination. It’s a crucial component of public safety, environmental sustainability, and urban planning. Smart street lighting can brighten as pedestrians pass, dim during quiet hours, and respond to real-time needs. It can even adjust brightness based on traffic patterns.
The magic behind this smart lighting is sensors and smart controls. You might be familiar with one of the most common lighting controls - Zigbee. However, LoRaWAN is also widely used in smart cities. So today, let’s talk about another lighting control for smart cities - LoRaWAN, and explore how it enables smart street lighting.
What is LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN, short for Long Range Wide Area Network, is a wireless communication protocol for the Internet of Things (IoT). It enables devices to communicate over vast distances.
Here are two key features of LoRaWAN:
- Long range: LoRaWAN operates over several kilometers, making it ideal for applications that require wide coverage. Even in densely populated urban areas, LoRaWAN can provide seamless connectivity across vast networks of streetlights, allowing for centralized monitoring and control.
- Low power consumption: LoRaWAN devices can operate on battery power for years. By minimizing energy usage during transmission and sleep modes, LoRaWAN extends the lifespan of devices and reduces maintenance efforts.
How LoRaWAN enables smart street lighting
LoRaWAN stands out as a pivotal factor in the realm of smart street lighting. With LoRaWAN, streetlights are becoming data-driven, adaptive, and interconnected. What components does a LoRaWAN lighting system include? How exactly does it enable smart street lighting?
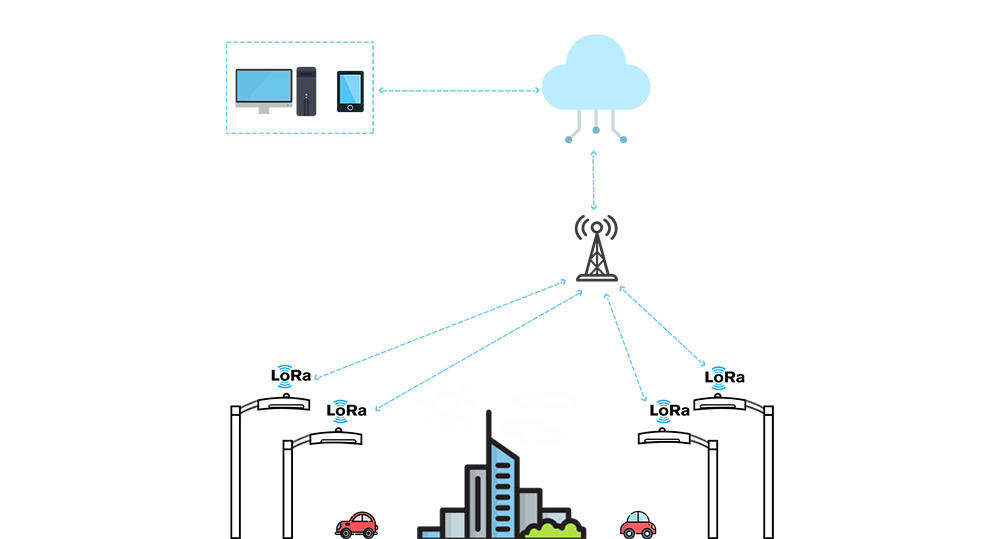
Components of LoRaWAN lighting systems
LoRaWAN-enabled streetlights: These are streetlights equipped with LoRaWAN-compatible sensors and communication modules. They continuously gather data on ambient light levels, motion detection, and other environmental factors, transmitting this information to the gateways.
Gateways: The gateways act as intermediaries, receiving data from multiple end devices within their range and relaying it to the server. Gateways are strategically placed throughout the city to ensure comprehensive coverage and reliable communication.
Network Server: The network server is a centralized platform that manages and processes the data received from the gateways. This server acts as the brain of the operation, analyzing the incoming data, applying intelligent algorithms, and generating instructions for the end devices.
How a LoRaWAN-based Smart Lighting System Works
- Streetlights collect data on ambient light levels, motion detection, and other relevant parameters. This data is then transmitted via the LoRaWAN protocol to the nearest gateways within range.
- Gateways receive data from multiple end devices and forward it to the network server.
- The network server processes the incoming data, optimizes lighting levels, detects faults, and identifies maintenance needs.
- Based on the analysis, the network server sends instructions back to the streetlights through gateways.
- Streetlights act upon these instructions, adapting their behavior in real-time to maximize energy efficiency, ensure optimal performance, and enhance public safety.
Benefits of LoRaWAN smart lighting
LoRaWAN technology brings a lot of advantages to smart street lighting systems. Here are some major benefits:
Energy efficiency
LoRaWAN lighting systems can automatically adjust light levels based on real-time data, dimming or brightening as needed. This adaptive approach not only reduces energy consumption but also minimizes light pollution, contributing to a more sustainable urban environment.
Real-time operations and maintenance
With real-time data, LoRaWAN lighting systems can identify and detect faults in fixtures promptly. Thus, operators can address issues promptly, minimizing downtime and keeping streets well-lit.
Scalability and flexibility
The long-range communication capabilities of LoRaWAN make it well-suited for large-scale deployments across diverse urban landscapes. Whether retrofitting existing lighting systems or deploying new installations, operators can seamlessly expand their smart lighting networks to meet evolving needs and growth demands.
Interoperability with other smart city solutions
LoRaWAN lighting controls can be integrated with various IoT applications. Data from streetlights combined with traffic sensors, air quality monitors, and emergency systems lead to safer and more responsive cities.

Difference between Zigbee and LoRaWAN
Both Zigbee and LoRaWAN are beneficial for smart street lighting. Unsure which one to use for your street lighting projects? Here’s a breakdown of their differences to help you choose the right fit:
Range
Zigbee: Zigbee offers a shorter range of about 100 meters. This makes it ideal for dense, urban environments where streetlights are clustered close together.
LoRaWAN: LoRaWAN boasts a much larger range of up to 15 kilometers. This makes it perfect for sprawling cities where streetlights are spread over vast distances.
Data rate
Zigbee: Zigbee offers a higher data rate compared to LoRaWAN. This can be beneficial for applications requiring faster data exchange, such as real-time dimming adjustments based on momentary changes in traffic or light levels.
LoRaWAN: LoRaWAN prioritizes low power consumption over high data rates. This translates to lower data transmission but still allows for efficient communication over long distances.
Network setup
Zigbee: Setting up a Zigbee network requires a mesh network with multiple devices acting as routers to extend the signal. This can be more complex to manage in large-scale deployments.
LoRaWAN: LoRaWAN utilizes gateways that collect data from devices and forward it to the central platform. This setup is simpler to manage, especially for large-scale deployments.
Security
Zigbee: Zigbee offers standard security features for data encryption.
LoRaWAN: LoRaWAN has robust security and advanced encryption protocols to safeguard sensitive data transmission.
Frequency bands
Zigbee: Zigbee works in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. It may experience interference from other wireless devices operating at the same frequency.
LoRaWAN: LoRaWAN operates on license-free sub-GHz bands. This reduces interference and provides better coverage.
Cost
Zigbee: Zigbee technology and hardware might be slightly less expensive compared to LoRaWAN. However, the potential need for a more complex mesh network setup could impact the total project cost.
LoRaWAN: LoRaWAN might have a slightly higher initial cost. But the simpler network setup and lower maintenance requirements can lead to overall cost savings.
Here is a table about the differences between Zigbee and LoRaWAN lighting controls:
|
Feature |
Zigbee |
LoRaWAN |
|
Range |
About 100m |
Up to 15Km |
|
Data Rate |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Network Setup |
Mesh network (more complex) |
Gateways (simpler) |
|
Frequency Bands |
2.4 GHz |
Sub-GHz bands (license-free) |
|
Security |
Standard |
Robust |
From the table, we can conclude that Zigbee is more suitable for industrial monitoring or areas with streetlights in close proximity. In contrast, LoRaWAN is ideal for smart cities that prioritizes long-range communication with low energy consumption.













