Are you looking for ways to improve lighting design and energy efficiency? One often overlooked aspect is the use of lighting controls. Lighting controls are devices or systems that allow you to adjust the brightness, color, and timing of lights. They offers a range of benefits, from creating the perfect ambiance, enhancing comfort and productivity to reducing energy consumption and carbon footprint.
But not all lighting controls are created equal. There are different types of lighting controls, such as switches, dimmers, timers, and sensors, each with its own pros and cons.
In this article, we will explore the different types of lighting controls available and the pros and cons of each. By the end of this blog, you will have a better understanding of differences of each type of lighting controls. So read on and discover the best lighting control solutions for you.

Traditional switches
switches are devices that allow you to turn lights on or off by completing or breaking the electrical circuit. They are the most common types of lighting controls and can be found in a variety of settings, from homes and offices to industrial and outdoor facilities.
One of the main advantages of traditional switches is their simplicity. They are easy to use and require no additional equipment or installation. They also provide instant and clear feedback. Second, switches are of low costs. Compared to other types of lighting controls, traditional switches are relatively inexpensive.
One issue about traditional switches is that they have limited functionality. They can only turn the lights or off, which may not be ideal for all lighting applications. Another issues is that they require manual operation, which can be inconvenient or impractical in certain situations, especially for large facilities or outdoor areas.
Dimmers
Dimmers are a popular and versatile type of lighting control that allow you to adjust the level of light in a space. They work by regulating the amount of electrical current supplied to the light fixture, allowing you to dim or brighten the light as desired.
The benefits of dimmers are many. First, they can help you save energy and money by reducing the power consumption and extending the lifespan of fixtures. Dimming a light by 25% can save about 20% of energy and increase the build life by four times. Another benefits are they are versatile. You can customize the light level according to your preference and acclivity.
The drawbacks of dimmers are flickering and compatibility issues. These can be annoying or even hazardous, particularly in settings where visual performance is important, such as in a workplace or sport evens for TV broadcast.
Timers
Timers are a type of lighting controls that allow you to set specific times for lights to turn on and off. They can be either analog or digital, and can be integrated with switches or fixtures. They can also be programmed to follow a daily, weekly, or seasonal pattern.
By automatically turning lights on and off at predetermined times, timers can help save energy and reduce costs. This can translate into significant cost savings over time, especially in setting where lighting costs can be major expense. Timers help improve security and convenience by providing automatic lighting for certain areas or events.
However, timers may cause complexity or difficulty in setting up and adjusting the schedule. If the you’s schedule changes or if they want to adjust the lighting for a specific event, they may need to manually override the timer, which can be inconvenient.
Sensors
Sensors work by detecting changes in the environment and then sending signals to the lighting system to adjust the light output accordingly. There are two main types of sensors used in lighting control: occupancy sensors (motion sensors) and photosensors.
Occupancy sensors (motion sensors)
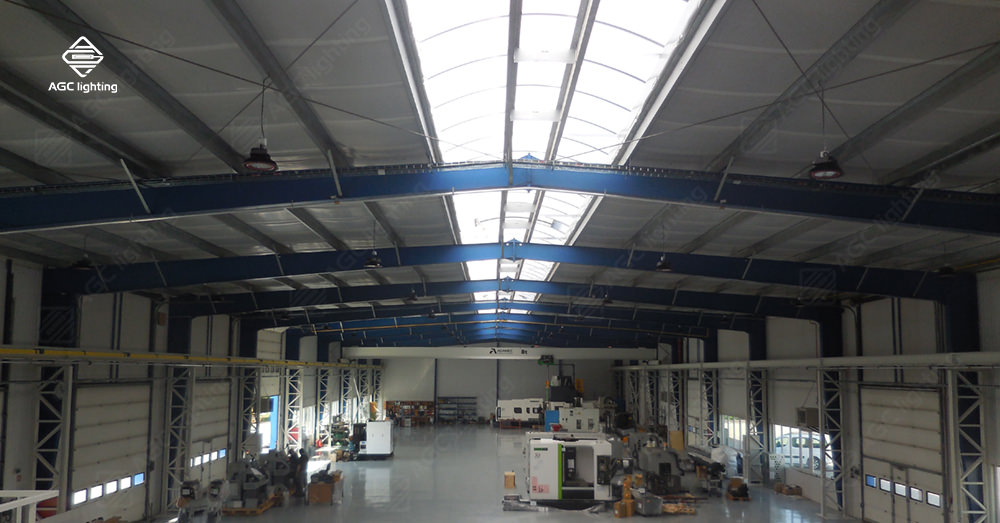
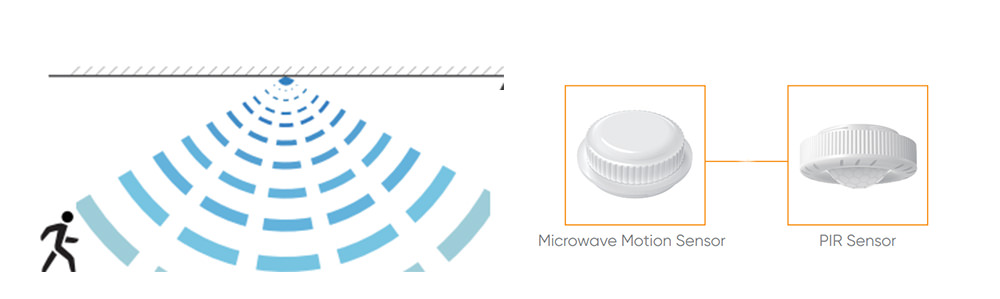
Occupancy sensors and motion sensors are often used alternately. They are ideal for outdoor applications. Occupancy sensors are designed to detect when people are present in a space and adjust the lighting accordingly. They turn the lights on when they sense someone entering a space and turn them off when they sense no one is present. Motion sensors are devices that detect movement of objects or people and turn on a light. There are different types of motion sensors, such as PIR and microwave sensors.
Occupancy sensors help reduce energy consumption and electricity costs. They prevent unnecessary lighting and save energy. Occupancy sensors also bring conveniences and improve safety. You don’t have to worry about manually turning lights on and off. Occupancy sensors will provide automatic lighting for dark or unoccupied areas, such as parking lots, roadways, and parks.
But motions sensors also have disadvantages. Microwave sensors can be blocked by metal objects or walls. Then they cannot trigger light to turn on even when there is a motion. PIR sensors can be triggered by any moving object, such as animals or insects, resulting energy waste. This can cause the lights to turn on and off unnecessarily, which can be annoying or distracting.
Photosensors
Photosensors also known as daylight sensors. They are designed to detect the level of ambient light in a space and adjust the lighting accordingly.
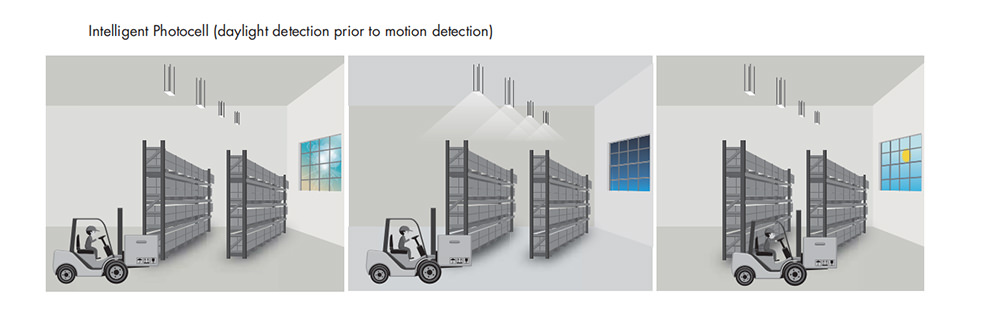
One of the main benefits of photosensors are they energy efficiency. For example, lighting fixtures in warehouses fitted with daylight sensor can automatically adjust the lighting based on natural light levels. They can help reduce energy consumption and extend the lifespan of fixtures. This can translate into significant cost savings over time.
However, photosensors can also have some potential drawbacks. One issue is their sensitivity to changes in natural light levels, which can sometimes cause the lighting to fluctuate or appear uneven. This can be particularly problematic in settings where visual performance is important, such as in a workplace or car repairing shop.
To conclude, here is a table about the pros and cons of different lighting controls.
|
Lighting Controls |
Feature |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Traditional switches |
Turn lights on or off by completing or breaking the electrical circuit |
Easy to use; Low cost |
Limited functionality; Require manual operation |
|
Dimmers |
Adjust the level of light in a space |
Save energy and money; Customize the light level according to your preference |
Flickering; Compatibility issues |
|
Timers |
Set specific times for lights to turn on and off |
Save energy and reduce costs; Improve security and convenience |
Complexity or difficulty in setting up and adjusting the schedule |
|
Occupancy sensors (Motion sensors) |
Detect when people are present or motion in a space and adjust the lighting accordingly |
Reduce energy consumption and electricity costs; Bring conveniences and improve safety |
Can be blocked by metal objects or walls; False triggers |
|
Photosensors (Daylight sensor) |
Detect the level of ambient light in a space and adjust the lighting accordingly |
Energy efficiency; Extend the lifespan of fixtures |
Fluctuate or uneven lighting
|
While each lighting control has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, many businesses choose to integrate multiple systems to achieve optimal results. One example of an integrated lighting system is the combination of daylight sensors and motion sensors for warehouses lighting.
Besides sensor-based controls, there are also various smart lighting solutions that can further optimize energy consumption. These solutions include simple on/off switches and sophisticated systems that use smart lighting protocols, such as DALI, Zigbee, and Casambi wireless lighting control, to enable flexible and customizable lighting control. If you are interested in learning more about our smart lighting solutions, please feel free to contact us.












