Smart lighting offers unparalleled convenience and energy efficiency in our lives. With just a tap on your smartphone or computer, you can control the light intensity or even light colors, creating the perfect ambiance for any space. However, as with any wireless technology, Bluetooth-based smart lighting systems can sometimes face interference, leading to frustrating connectivity issues and disruptions.
Is there any way to reduce Bluetooth interference?
Of course yes.
In this post, we will talk about the Bluetooth interface and show you some practical steps to minimize Bluetooth interference, ensuring a smooth smart lighting system.
What is Bluetooth interference?
Have you ever experienced the frustration of smart lights refusing to cooperate, dimming erratically, or responding with annoying delays? This is the presence of Bluetooth interference.
At its core, interference occurs when other wireless signals or devices in the vicinity disrupt or interfere with the Bluetooth signal used by your lighting fixtures and controllers. The interference can manifest in various ways, ranging from intermittent connectivity to delayed response times and even complete signal loss.
What causes Bluetooth interference
To effectively minimize interference, it's essential to understand the common causes that can disrupt the Bluetooth signal and compromise the performance of your smart lighting system. The common reasons for Bluetooth interference are as below:
Overlapping frequencies
One of the most common causes of interference is the presence of other wireless devices operating on the same or adjacent frequency bands as Bluetooth. Wi-Fi networks, for instance, can interfere with Bluetooth signals, as they operate in the 2.4 GHz range. Similarly, microwave ovens, cordless phones, and even certain types of baby monitors can contribute to interference by emitting electromagnetic radiation that overlaps with Bluetooth frequencies.
Physical barriers
Physical barriers can also contribute to Bluetooth interference. Walls, floors, and equipment can obstruct the Bluetooth signal, especially if they are made of materials that are known to impede wireless transmission. This must be taken into account when designing a luminaire and placing it in applications.
- Materials in the walls: Fine-meshed metal textures or materials used in walls, especially in older buildings, can suppress or attenuate radio communication signals.
- Windows and panes: Windows and panes with sun protection coatings, which often contain metal, can also severely attenuate radio signals.
- Metal: Metal is an extreme example of a material that can block or greatly hinder the passage of radio waves. If a radio transmitter is completely surrounded by metal, it acts like a Faraday cage, preventing any radio waves from escaping.
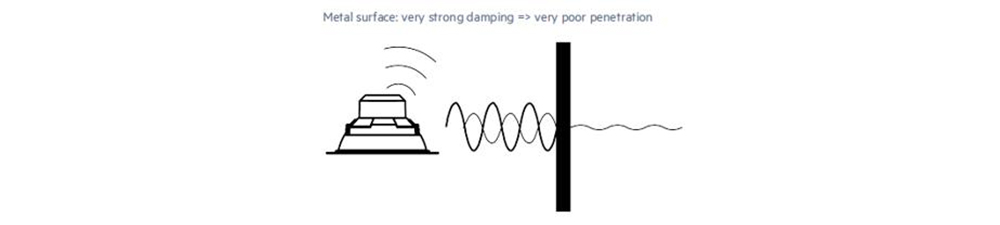
Here is a chart of the interference level of different materials when using Bluetooth:
|
Low Interference |
Medium Interference |
High Interference |
Very High Interference |
|
Wood |
Water |
plaster |
Metal |
|
Glass |
Bricks |
Concrete |
|
|
Synthetic materials |
Marble |
Bulletproof glass |
|
The Device duel
The placement and configuration of your Bluetooth-enabled devices can play a role in interference. Devices positioned too close together or in areas with high electromagnetic interference can experience signal degradation or conflicts.
Distance
The distance between devices can also play a role, as the Bluetooth signal weakens over longer distances.
So please notice the floor plan of the building and avoid long corridors when using Bluetooth lighting control. Well-functioning networks have a circular structure with few hops. You should keep the distance between luminaires as short as possible (but less than the maximum range of a luminaire).
Tips to minimize Bluetooth interference
Minimizing Bluetooth interference in your smart lighting setup is essential for enjoying a seamless and hassle-free experience. By implementing the right strategies, you can overcome connectivity issues, reduce disruptions, and unlock the full potential of your intelligent lighting system. Here are some practical tips to help you tackle Bluetooth interference head-on:
Strategic Placement of Devices
The placement of your Bluetooth devices plays a crucial role in mitigating interference. Start by ensuring that your smart lighting fixtures and controllers are positioned away from potential sources of interference, such as Wi-Fi routers. Maintain a reasonable distance between these devices to minimize signal overlap and interference.
Additionally, consider the physical layout of your space. Avoid placing Bluetooth devices near thick walls, metal surfaces, or large appliances, as these can block or reflect wireless signals, leading to dead zones or weak connectivity.
Frequency Management
Bluetooth operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, which is also used by many other wireless technologies. To minimize interference, explore frequency management techniques that allow you to select specific channels or frequency hopping patterns for your other devices that can cause interference.
So please notice other radio systems available on site, like WLAN, Thread, ZigBee, etc.
Using Bluetooth Range Repeaters
Unfavorable building layouts can lead to “island problems”. An “island problem” occurs if a single network is divided into multiple non-contacting networks due to the physical nature of the building. If you're experiencing Bluetooth interference due to distance limitations, consider using Bluetooth range extenders or repeaters. These devices can amplify the Bluetooth signal and extend the range, ensuring that your smart lighting devices can communicate reliably even in larger spaces or areas with physical barriers. Another way to solve the “island problems” is to split the network into smaller individual networks.
Shielding and Separation
Physical barriers and shielding can effectively reduce the impact of interference on your Bluetooth connections. Consider using materials like aluminum foil or specialized shielding paints to create a barrier between your Bluetooth devices and potential sources of interference.
Additionally, maintaining separation between Bluetooth devices and other wireless equipment can help mitigate interference. If possible, place your smart lighting controllers or hubs in a different room or area from your Wi-Fi router or other wireless devices.
Software Updates and Firmware Optimization
Manufacturers regularly release software updates and firmware patches that can improve Bluetooth performance and mitigate interference issues. Ensure that your smart lighting system, including fixtures, controllers, and associated apps, is up-to-date with the latest software versions.
These updates often include optimizations and bug fixes that can enhance Bluetooth connectivity, reduce interference, and improve overall system stability. Check with your manufacturer for available updates and follow their instructions for seamless installation.













