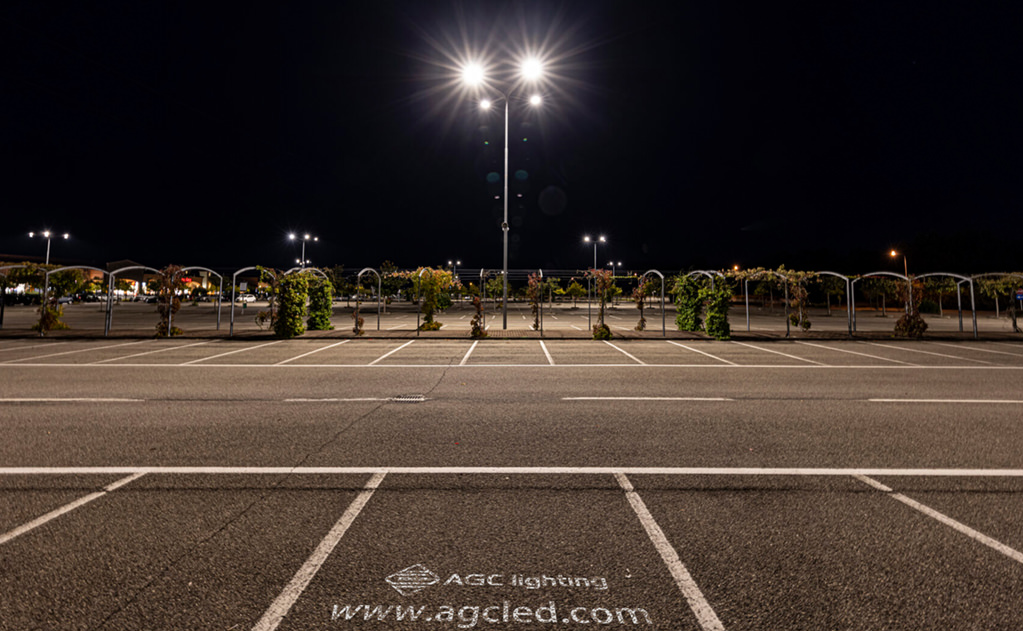
Lighting plays an important role in ensuring the safety and security both of drivers and pedestrians. Most of the parking lot fixtures are mounted on poles to cover larger lighting areas. Requirements of different places vary from each other. Parking lot lighting is supposed to be comfortable without strain on eyes. Different applications have their own lighting standards. For example, a large shopping mall has more complex parking lot lighting needs than rural and residential parking lots. Thus, there are no uniform methods to select appropriate fixtures for every application.
In this article, we'll guide you through the key considerations and steps to choose the best outdoor parking lot LED lighting.
Firstly, measure your parking lot
Only carefully measuring your parking lot, can you know the size and how to arrange the fixtures. Sketch the parking lot according to the measured dimensions, and then decide how to place the fixtures. A proper layout can help you place fixtures efficiently, increasing space utilization and reducing energy costs. Parking lots with a larger area certainly need more fixtures and fixtures with higher illuminance. But remember that more fixtures do not equal a better lighting experience, lighting performance should be taken into account as well.
Secondly, think about lighting performance
When it comes to lighting performance, illuminance, color rendering index, correlated color temperature, lighting distribution, and resistance to outdoor environment are supposed to be considered. Premium lighting performance will favor environments and facial recognition, which makes people feel safer.
Illuminance
Illuminance is a term that describes the amount of luminous flux illuminating a surface, per unit area. Parking structures require an average illumination of 54 lux, while parking lots only require 10 lux.
There are horizontal and vertical illuminance for parking lot lighting. Horizontal illuminance means the lighting levels measured on ground surfaces. Vertical illuminance is the lighting level measured 90 degrees from the nadir on an average height of 1.5 meters from the ground.
Signage, facades of the building, and trees or other vegetation should be considered as vertical lighting elements. To avoid cars or pedestrians shaded by them, place the fixtures away from them, or offer a higher illuminance for clearer visibility. The following table shows the recommended illuminance values for parking lots.
|
Application |
Recommended illuminance targets (lux) |
|
|
Horizontal min |
Vertical min |
|
|
Asphalt surfaces |
2-5 |
1-2.5 |
|
Concrete surfaces |
2-10 |
1-5 |
|
Transaction areas |
2-10 |
1-5 |
Color rendering index
The Color Rendering Index is the ability to reflect the true color of an item. The closer the color rendering index is to 100, the more natural the colors of the product will appear. The LED lights with the ability to reveal the exact color of the objects are important to the vision of people.
A color rendering index equal to or less than 60 refers to poor color rendering performance. However, there is no need to pursue the highest color rendering index as the cost would increase with the greater values. Generally speaking, a color rendering index above 70 is sufficient for most parking lots.
CCT (Correlated Color Temperature), indicates the hue of a light source. What we usually explain as “cool white” or “warm white” refers to CCT. The CCT of warm light is less than 3500K while the cool light is higher than 4500k. The range of CCT from 3500k to 5000k is suitable for most of parking lots. The natural white light is comfortable for the human eye.
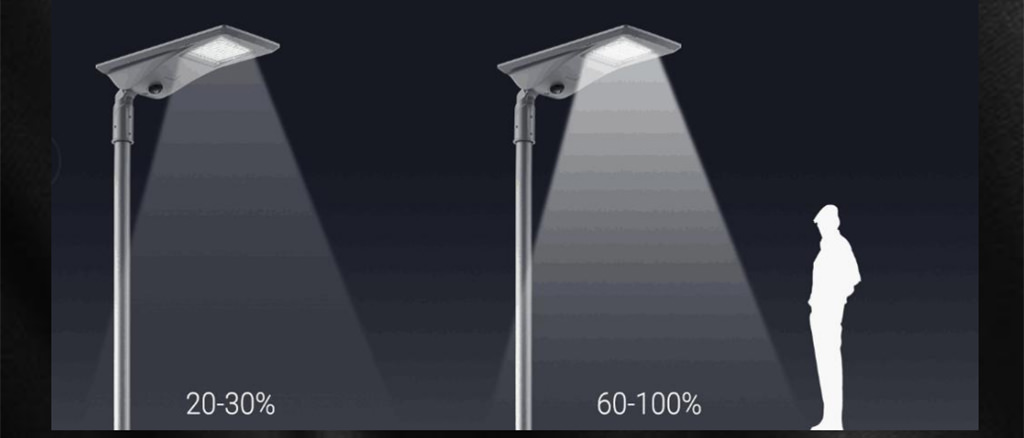
Lighting distributions
Parking lots are not isolated but located around business buildings, residential areas, schools, etc. Thus, human activity will be affected by parking lot lighting distribution. Qualified parking lot lighting should be bright enough and minimize glare, backlight, and uplight.
That is where the BUG rating comes in parking lot lighting. BUG rating refers to an outdoor lighting distribution and light pollution potential. “B” for backlight, “U” for light directed upward above the horizontal plane of the luminaire, and “G” for glare (high-angle forward light). BUG rating evaluates the optical performance of lighting trespass, sky glows, and high angle brightness.
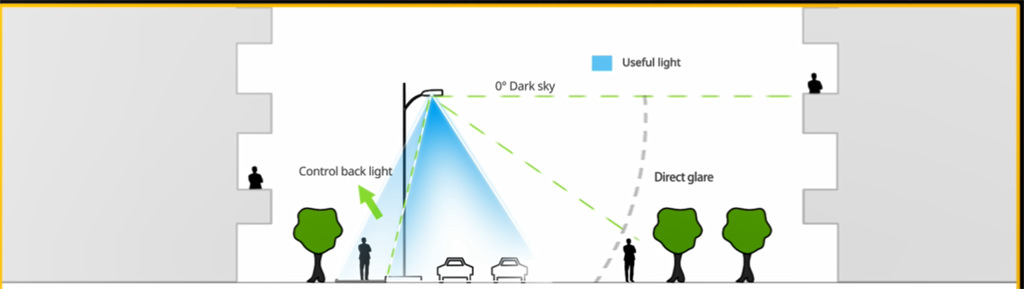
For parking lost near residential areas, Type Type II, III, or IV light distributions can minimize backlight and prevent light trespass to windows of homes.
Learn More about Lighting Distribution Types
Durability and environmental factors
Parking lot fixtures are faced with long-term exposure to the sun, wind, rain, extreme high or low temperatures. The harsh environment of the parking lot requires high-quality fixtures. Resistance to water, dust, impact, and corrosion are the main factors for a parking lot fixture to withstand a cruel environment. The corresponding standards are IP rating, IK rating, and corrosion resistance.
IP (Ingress Protection) is an internationally recognized scale that indicates the degree of protection of electrical equipment enclosures against the intrusion of foreign objects. The protection level is mostly expressed by two numbers followed by IP. The numbers are used to specify the level of protection.
IK rating consists of two numbers, namely IK01, IK02, IK03, IK04, IK05, IK06, IK07, IK08, IK09 and IK10. The higher the number is, the better the protection. Generally, the fixtures with the IK code higher than IK08 can withstand most of the mechanical impact, and the lights with the IK10 rating are equipped with the highest protection.
Corrosion is the process of loss and damage of objects (including metal and non-metal) under the action of surrounding media (water, air, acid, alkali, salt, solvent, etc.). The best solution to avoid corrosion is to isolate LED light from hazardous materials and the environment. Thus, manufacturers use stable materials and add coating film for fixtures to prevent corrosion.
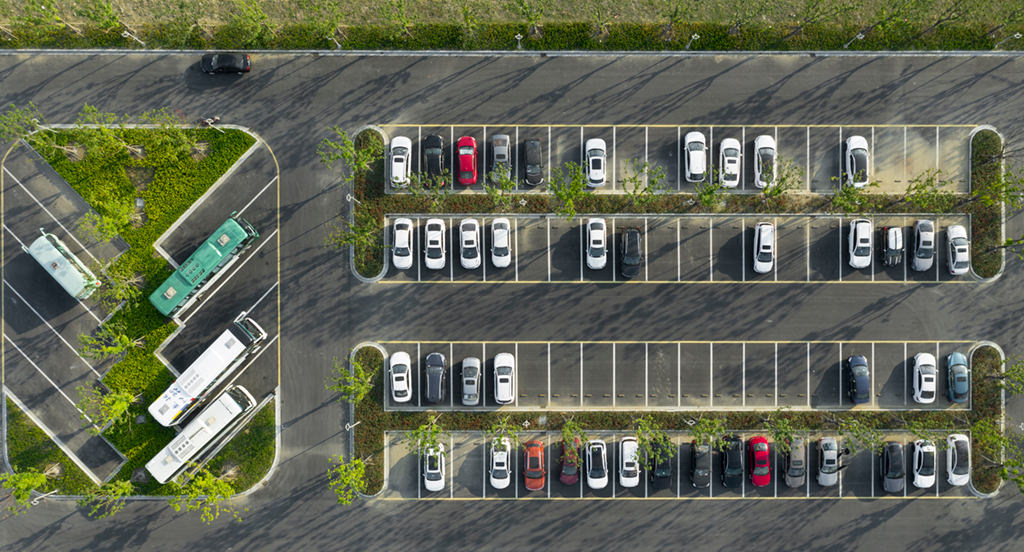

Thirdly, consider the external cost
Except for the cost of purchasing fixtures, payments of energy consumption, installation, replacement, and maintenance are also critical for cost management. Deeper consideration of total cost can help you save potential expenditures.
Energy cost
Energy-saving fixtures are able to convert input to output effectively, in other words, converting electricity into more photic energy. When we select the fixture for the parking lot, we should concerned about efficacy, which is measured in lumen per watt. The higher the values are, the greater the efficacy. Compared to conventional lights, 30% to 70% energy saving can be achieved by LED lights. A longer lifespan of fixtures can decrease average energy costs as well. Installing adaptive controls can reduce working times and energy waste.
Installation & replacement cost
Parking lot fixtures are commonly mounted on poles with appropriate height to provide sufficient lighting. Installation costs a lot due to the employment of qualified technicians. Foundation and trench for providing power to poles and the poles themselves are of high price. The total cost of poles may exceed the cost of fixtures in some conditions. A significant labor cost is also required for replacing parking lot fixtures. Therefore, if you would like to retrofit the parking lot lighting system, reuse the existing poles if possible.
Maintenance cost
When failure occurs, there is a requirement to use a bucket truck or lift to mend the fixtures as fixtures are often mounted on poles in the height excess of 15ft. However, not every buildings or facilities have a bucket truck or lift. In consequence, hiring the tools and technicians for mend is necessary. The maintenance cost is unpredictable. Therefore, tough manufacturers provide warranties that may be longer than the lifespan of fixtures, concerned about the maintenance cost as well.
Lastly, determine whether to incorporate lighting controls
Parking lots are lit for a long time per day. In certain periods at night, the parking lots are free of vehicles or pedestrians. The usage of controls is one step towards energy savings and cost-effective lighting systems. Photosensors, time clocks, astronomical time clocks, and motion detectors are typically used for lighting controls.
Photosensors
Photosensors turn on or off the fixtures in terms of the amount of natural light. The housing, optics, electronics, and photocell consist of photosensors. With the assistance of photosensors, parking lot fixtures are turned off when there is sufficient daylight and turned on at sunset to reduce energy waste. The disadvantages of photosensors are the false trigger during climatic changes and the shorter life compared to fixtures.
Time clock
Time clock controls are often used with a combination of photosensors. Thus, fixtures are turned off or dimmed at a certain time. Time clock controls contribute to saving energy at night or after business time.
Astronomical time clock
Astronomical time clock controls adjust the on and off fixtures according to the predicted times of sunset and sunrise, which are based on the location of the parking lot. Though astronomical time clock controls are not affected by the available daylight, they cannot detect heavy clouds. As a result, there is a risk of inaccurate control.
Motion detectors
Motion detectors are triggered by the movement of vehicles and pedestrians. They are usually used for entry as well as the interior. The dynamic response allows more energy saving without time or daylight limitations.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into choosing the best outdoor parking lot lighting for your property. If you have any further questions or need assistance with your lighting projects, feel free to contact us.